Cluster federation
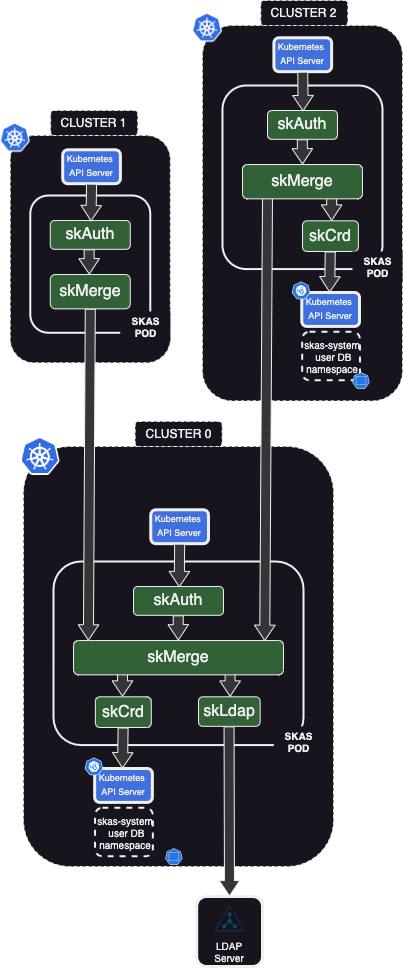
Due to its modular concept and the ability to configure links between modules, even across clusters, SKAS is very effective in a multi-cluster environment.
Here's a sample configuration to illustrate this:
Cluster0serves as a kind of 'control' cluster, acting as a 'hub' and providing centralized user information. It can be dedicated to this role or host other control functions.Cluster1is a standard cluster that hosts typical workloads. It relies entirely onCluster0for user authentication.Cluster2is similar toCluster1, but it can also manage some local users and/or groups."
Of course, this is just one example of what could be achieved with SKAS.
In the rich Kubernetes ecosystem, there are several solutions, such as Submariner, Skupper, Cilium ClusterMesh, Liqo, and more, aimed at extending the concept of Kubernetes
servicesacross clusters. While these can be used in our cases, the configuration described here relies on 'pure vanilla', independent Kubernetes clusters.

Cluster0 deployment.
Here are two samples of value files for cluster0
- One with only the local user database.
- Another one with also an external LDAP server.
The LDAP server sample will help illustrate the chaining of providers.
Here is the values file with only the local user database (It is activated by default):
values.cluster0-noldap.yaml
clusterIssuer: your-cluster-issuer
skAuth:
exposure:
external:
ingress:
host: skas.ingress.cluster0
kubeconfig:
context:
name: skas@cluster0
cluster:
apiServerUrl: https://kubernetes.ingress.cluster0
skMerge:
exposure:
external:
enabled: true
services:
identity:
disabled: false
clients:
- id: cluster1
secret: cluster0Cluster1SharedSecret
- id: cluster2
secret: cluster0Cluster2SharedSecret
ingress:
enabled: true
host: skas-skmerge.ingress.cluster0
The first part includes what was previously in a separate values.init.yaml file in other samples within this
documentation. Consequently, this file can be used for the initial deployment or for upgrading an existing one.
Then, there is the part specific to this configuration. The identiy service of the
skMerge module is exposed externally, and authentication is required from the callers, which will be the two
other clusters.
Furthermore, this service must be accessed externally. So, set ingress.enable: true and adjust the ingress.host
value to your specific context.
Remember that the
ingress.hostvalue must also be defined in your DNS.
Here is the values file, including the LDAP external server as well:
values.cluster0-ldap.yaml
clusterIssuer: your-cluster-issuer
skAuth:
exposure:
external:
ingress:
host: skas.ingress.cluster0
kubeconfig:
context:
name: skas@cluster0
cluster:
apiServerUrl: https://kubernetes.ingress.cluster0
skLdap:
enabled: true
# --------------------------------- LDAP configuration
ldap:
host: ldap.mydomain.internal
insecureNoSSL: false
rootCaData: "LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZ................................lRJRklDQVRFLS0tLS0K"
bindDN: cn=Manager,dc=mydomain,dc=internal
bindPW: admin123
groupSearch:
baseDN: ou=Groups,dc=mydomain,dc=internal
filter: (objectClass=posixgroup)
linkGroupAttr: memberUid
linkUserAttr: uid
nameAttr: cn
timeoutSec: 10
userSearch:
baseDN: ou=Users,dc=mydomain,dc=internal
cnAttr: cn
emailAttr: mail
filter: (objectClass=inetOrgPerson)
loginAttr: uid
numericalIdAttr: uidNumber
skMerge:
providers:
- name: crd
- name: ldap
exposure:
external:
enabled: true
services:
identity:
disabled: false
clients:
- id: cluster1
secret: cluster0Cluster1SharedSecret
- id: cluster2
secret: cluster0Cluster2SharedSecret
ingress:
enabled: true
host: skas-skmerge.ingress.cluster0
Please refer to LDAP Setup for instructions on how to configure the connection to this external LDAP server.
To apply the choosen configuration, please ensure that you have a kubectl configuration set up to target cluster1
with administrator privileges, and then enter one of the following commands:
helm -n skas-system upgrade -i skas skas/skas --values ./values.cluster0-noldap.yaml --create-namespace
or:
helm -n skas-system upgrade -i skas skas/skas --values ./values.cluster0-ldap.yaml --create-namespace
If this is the first deployment on this cluster, don't forget also to configure the API Server
For the configuration of the two other clusters, you will need the Certificate Authority of the ingress on the
skMerge identity endpoint, encoded in base64. You can retrieve it with the following command:"
Cluster1 deployment
Here is a sample values file for the deployment of cluster1:
values.cluster1.yaml
clusterIssuer: your-cluster-issuer
skAuth:
exposure:
external:
ingress:
host: skas.ingress.cluster1
kubeconfig:
context:
name: cluster1
cluster:
apiServerUrl: https://kubernetes.ingress.cluster1
skMerge:
providers:
- name: cluster0
providerInfo:
cluster0:
url: https://skas-skmerge.ingress.cluster0
rootCaData: "LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRV.............09Ci0tLS0tRU5EIENFUlRJRklDQVRFLS0tLS0K"
insecureSkipVerify: false
clientAuth:
id: cluster1
secret: cluster0Cluster1SharedSecret
skCrd:
enabled: false
Once again, the first part includes what was previously stored in a separate values.init.yaml file,
which has been used in other samples within this documentation.
Then, within the configuration:
- The
skMerge.providerslist contains only one provider:cluster0, which is defined just below it. - The
providerInfo.cluster0.urltargets the ingress we've set up oncluster0in order to reach its identity service. - The
providerInfo.cluster0.rootCaDatais configured with the base64-encoded Certificate Authority of the ingress on theskMergeidentity endpoint, as we obtained in the previous step. - The
providerInfo.cluster0.clientAuthprovides the required authentication information forcluster0.
To apply this configuration, please ensure that you have a kubectl configuration set up to target cluster1 with
administrator privileges, and then enter the following command:
If this is the first deployment on this cluster, don't forget also to configure the API Server
Testing
In the following, we will use the configuration where an LDAP server is connected to
cluster0.
We can now configure our local Kubernetes config file to authenticate to our clusters through SKAS:
$ kubectl sk init https://skas.ingress.cluster0
> Setup new context 'cluster0' in kubeconfig file '/Users/john/.kube/config'
$ kubectl sk init https://skas.ingress.cluster1
> Setup new context 'cluster1' in kubeconfig file '/Users/john/.kube/config'
We can connect as admin on cluster0 and check what this user looks like:
$ kubectl config use-context cluster0
> Switched to context "cluster0".
$ kubectl sk login admin
> Password:
> logged successfully..
$ kubectl sk user describe admin --explain
> USER STATUS UID GROUPS EMAILS COMMON NAMES AUTH
> admin passwordUnchecked 0 admin,all,auditors,skas-admin admin@xxxx.com SKAS administrator,admin crd
> Detail:
> PROVIDER STATUS UID GROUPS EMAILS COMMON NAMES
> crd passwordUnchecked 0 skas-admin SKAS administrator
> ldap passwordUnchecked 2003 all,auditors,admin admin@xxxx.com admin
In this example, the user admin exists in both of our providers (crd and ldap). Both sets of values are merged
to provide the user profile (Refer to Identity Providers chaining).
Now, we can perform the same operation on 'cluster1':"
$ kubectl config use-context cluster1
> Switched to context "cluster1".
$ kubectl sk login admin
> Password:
> logged successfully..
$ kubectl sk user describe admin --explain
> USER STATUS UID GROUPS EMAILS COMMON NAMES AUTH
> admin passwordUnchecked 0 admin,all,auditors,skas-admin admin@xxxx.com SKAS administrator,admin cluster0
> Detail:
> PROVIDER STATUS UID GROUPS EMAILS COMMON NAMES
> cluster0 passwordUnchecked 0 admin,all,auditors,skas-admin admin@xxxx.com SKAS administrator,admin
From the perspective of cluster1, we have only one provider: cluster0. We abstract away the details of how the
admin profile was constructed.
If we wish to expose this information, we can refactor this configuration by connecting
cluster1.skMergedirectly to thecluster0identity providers (crdandldap), one level belowskMerge.
Now, let's attempt to create a new user on cluster1:
$ kubectl config use-context cluster1
> Switched to context "cluster1".
$ kubectl sk whoami
> USER ID GROUPS
> admin 0 admin,all,auditors,skas-admin
$ kubectl sk user create localuser1 --generatePassword
> ERRO[0000] API server communication error error="users.userdb.skasproject.io \"localuser1\" is forbidden: User \"admin\" cannot get resource \"users\" in API group \"userdb.skasproject.io\" in the namespace \"skas-system\""
The operation fails because the admin user does not have the necessary permissions to write to the skas-system
namespace in cluster1. This behavior is intentional, as we intend for user definitions to exist exclusively in
cluster0.
There is a scenario where this operation might appear to succeed: If your admin user also has Kubernetes administrator
privileges (i.e., a member of system:masters), it will be able to write to the skas-system namespace, resulting
in a successful creation. However, it's important to note that users created in this manner will not be recognized
by the system in cluster1, as there is no crd provider present."
$ kubectl config use-context cluster0
> Switched to context "cluster0".
$ kubectl sk user bind admin system:masters
> GroupBinding 'admin.system.masters' created in namespace 'skas-system'.
$ kubectl config use-context cluster1
> Switched to context "cluster1".
$ kubectl sk login admin
> Password:
> logged successfully..
$ kubectl sk whoami
> USER ID GROUPS
> admin 0 admin,all,auditors,skas-admin,system:masters
$ kubectl sk user create localuser1 --generatePassword
> The following password has been generated: 'KTeZrzYEgeHS'
> (Save it as it will not be accessible anymore).
> User 'localuser1' created in namespace 'skas-system'.
$ kubectl sk login localuser1 KTeZrzYEgeHS
> Invalid login!
Cluster2 deployment
Here is a sample values file for the deployment of cluster2:
values.cluster2.yaml
clusterIssuer: cluster-issuer1
skAuth:
exposure:
external:
ingress:
host: skas.ingress.cluster2
kubeconfig:
context:
name: cluster2
cluster:
apiServerUrl: https://kubernetes.ingress.cluster2
# Members of these group will be allowed to perform 'kubectl-sk user describe'
# Also, they will be granted by RBAC to access token resources
adminGroups:
- skas-admin
- cluster2-skas-admin
skMerge:
providers:
- name: cluster0
- name: crd
providerInfo:
cluster0:
url: https://skas-skmerge.ingress.cluster0
rootCaData: "LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS...........VNGelVDQT09Ci0tLS0tRU5EIENFUlRJRklDQVRFLS0tLS0K"
insecureSkipVerify: false
clientAuth:
id: cluster2
secret: cluster0Cluster2SharedSecret
skCrd:
enabled: true
initialUser:
login: cluster2-skas-admin
passwordHash: $2a$10$ijE4zPB2nf49KhVzVJRJE.GPYBiSgnsAHM04YkBluNaB3Vy8Cwv.G # admin
commonNames: ["Cluster2 SKAS administrator"]
groups:
- cluster2-skas-admin
# Members of theses groups will be granted RBAC access to users and groupBinding resources in the namespace above
adminGroups:
- cluster2-skas-admin
- skas-admin
Once again, the first part includes what was previously stored in a separate values.init.yaml file,
which has been used in other samples within this documentation.
Then, within the configuration:
skMerge.providersreference now our localcrdproviders aside the globalcluster0.skMerge.providerInfo.cluster0is the same as forcluster1, except of course theclientAuthpart.- An initial user (
cluster2-skas-system) is created as local admin. This account will only be valid on this cluster. - The list of
adminGroupsmust be defined twice:- One in the
skAuthmodule. This is to allow thekubectl-sk user describecommand for members of these groups. - One in the
skCrdmodule. This is to set up RBAC rules to allow SKAS resources (skusers,groupBindings,tokens) to be managed by members of these groups.
- One in the
To apply this configuration, please ensure that you have a kubectl configuration set up to target cluster2 with
administrator privileges, and then enter the following command:
If this is the first deployment on this cluster, don't forget also to configure the API Server
Testing
We can now configure our local Kubernetes config file to authenticate to cluster2 through SKAS:
$ kubectl sk init https://skas.ingress.cluster2
> Setup new context 'cluster2' in kubeconfig file '/Users/john/.kube/config'
Now, we can log in as the local admin and describe ourself:
$ kubectl sk login cluster2-skas-admin
> Password:
> logged successfully..
$ kubectl sk user describe cluster2-skas-admin --explain
> USER STATUS UID GROUPS EMAILS COMMON NAMES AUTH
> cluster2-skas-admin passwordUnchecked 0 cluster2-skas-admin Cluster2 SKAS administrator crd
Detail:
> PROVIDER STATUS UID GROUPS EMAILS COMMON NAMES
> cluster0 userNotFound 0
> crd passwordUnchecked 0 cluster2-skas-admin Cluster2 SKAS administrator
Ensure we can perform all usual user management operations with this account:
$ kubectl -n skas-system get tokens
> NAME CLIENT USER LOGIN AUTH. USER ID CREATION LAST HIT
> tjvygwmtparktpwiiuysydzctbunppkycsykprtdswsramtm cluster2-skas-admin crd 0 2023-08-31T12:43:03Z 2023-08-31T12:43:26Z
$ kubectl sk user create cluster2user1 --generatePassword
> The follwing password has been generated: '8fJoM6JFObjO'
> (Save it as it will not be accessible anymore).
> User 'cluster2user1' created in namespace 'skas-system'.
$ kubectl sk user bind cluster2user1 cluster2grp1
> GroupBinding 'cluster2user1.cluster2grp1' created in namespace 'skas-system'.
$ kubectl sk user describe cluster2user1
> USER STATUS UID GROUPS EMAILS COMMON NAMES AUTH
> cluster2user1 passwordUnchecked 0 cluster2grp1 crd
$ kubectl sk user describe cluster2user1 --explain
> USER STATUS UID GROUPS EMAILS COMMON NAMES AUTH
> cluster2user1 passwordUnchecked 0 cluster2grp1 crd
> Detail:
> PROVIDER STATUS UID GROUPS EMAILS COMMON NAMES
> cluster0 userNotFound 0
> crd passwordUnchecked 0 cluster2grp1
And check if the newly created user is effective:
$ kubectl sk login cluster2user1 8fJoM6JFObjO
> logged successfully..
$ kubectl sk whoami
> USER ID GROUPS
> cluster2user1 0 cluster2grp1
$ kubectl get ns
> Error from server (Forbidden): namespaces is forbidden: User "cluster2user1" cannot list resource "namespaces" in API group "" at the cluster scope
The same operations can also be performed using the
adminaccount because it is a member of theskas-admingroup, which we have included in the twoadminGroupslists in thevalues.cluster2.yamlconfiguration file.